By Eric Ries.
A brief summary of the book The Lean Startup by Eric Ries. The Lean Startup offers a semi-scientific approach to build a profitable business by using
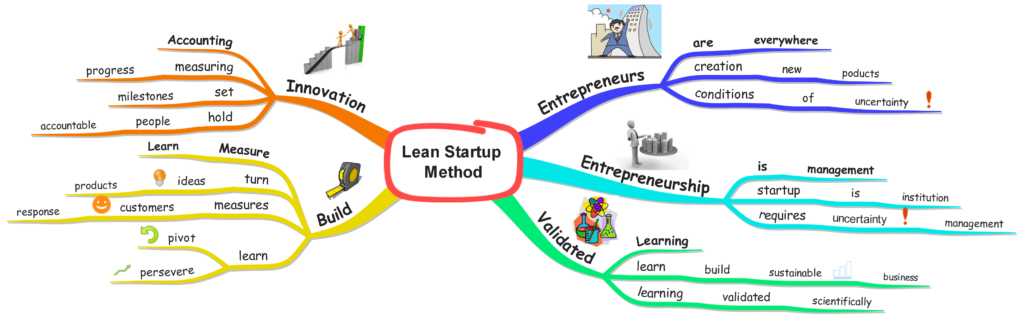
You can find the full size Mindmap here.
- Introduction
- Part 1: Vision
- Chapter 1: Start
- Chapter 2: Define
- Chapter 3: Learn
- Chapter 4: Experiment
- Part Two: Steer
- Chapter 5: Leap
- Chapter 6: Test
- Chapter 7: Measure
- Chapter 8: Pivot (or Persevere)
- Part 3: Accelerate
- Chapter 9: Batch
- Chapter 10: Grow
- Chapter 11: Adapt
- Chapter 12: Innovate
- Chapter 13: Epilogue: Waste Not
- Final Advice On Executing Lean Startup
What is Lean Startup ?
Lean manufacturing/production involves:
- Know your customer
- Eliminate waste
- Shrink batch size
- Just-in-time production
- Acceleration of cycle times
Principles of Lean Startup
- Entrepreneurs are everywhere
- Entrepreneurship is management
- Validate learning
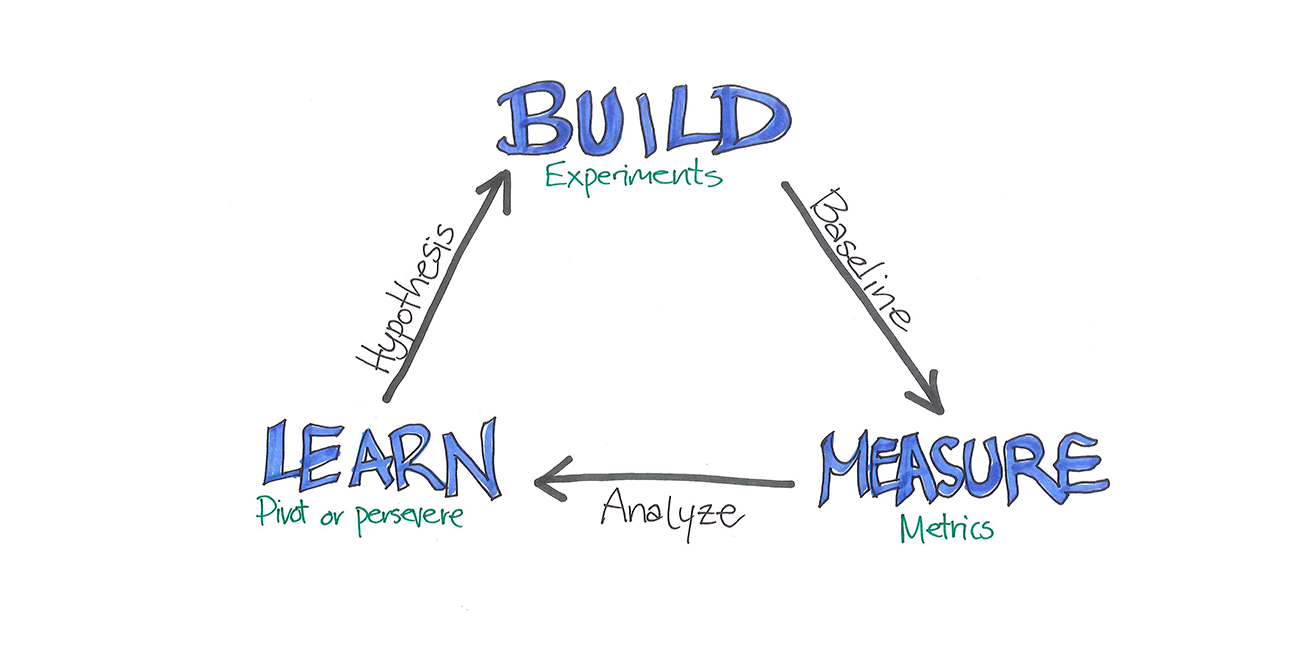
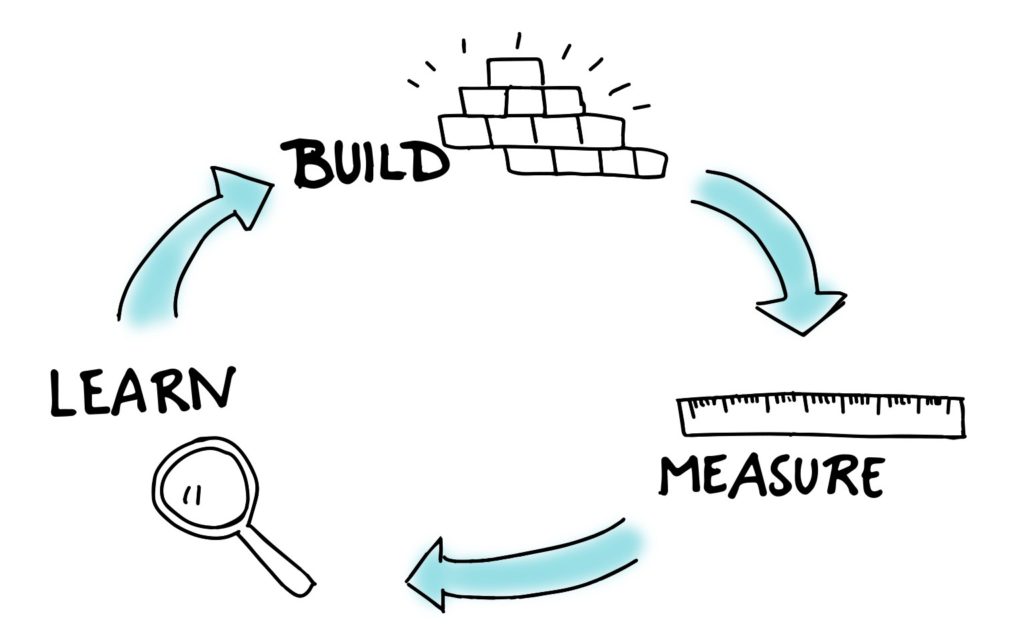
- Build – Mesure – Learn
- Innovative accounting
The Lean Pyramid
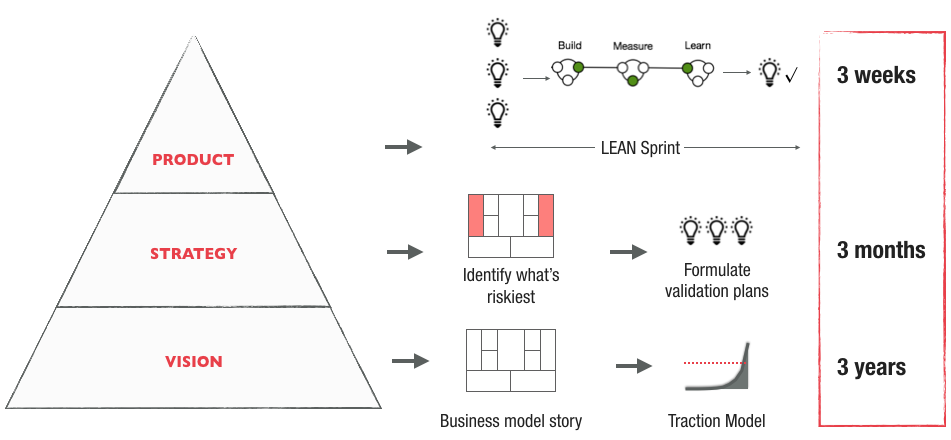
- Vision: Where you thrive to reach
- Strategy: Business model, road map,…
- Product: End result of the strategy
The Vision
The startup
Always measure progress, evaluate performance locally, if the tests
You should break down the larger vision in little experiments and gather customer responses.
To experiment define a clear hypothesis by making initial assumptions, you can use the
Genchi Genbutsu (Go and see for yourself)
Genchi Genbutsu is the key principle in the Toyota production system. It facilitates early contact with potential customers. It ensures that actual issues and unplanned events will be observed first hand.
Quality Principle
If we do not know who the customer is, we do not know what quality is. Do not give for granted what the customer will find useful and what he will not. Always cycle test and adjust using customer feedbacks. Remove any feature that isn’t useful for the customer.
Split tests & Metrics
Split tests are experiments where different versions of the product are offered to the client at the same time.
You need to choose the right metrics to measure the progress and avoid using VANITY METRICS (facebook likes, followers on
Good metrics should be actionable, accessible and auditable.
PIVOT OR PERSEVERE
Pivot is a structured change aiming to test a new fundamental hypothesis. But what are the signals that we should pivot? Do PIVOT or PERSEVERE meetings will all the team and use your metrics to decide.
Pivot require courage.
A startup runaway is the number of pivots it can still do.
ACCELERATE
When the metrics are positive, the Startup
A batch is a work that moves from one stage to the next at a time. Using large batches will decrease productivity in the team and quality in your product.
Adopt the ONE PIECE FLOW strategy!
GROWTH (traction)
New customers will come from the feedback of past customers. Treat them well.
- Sticky
- Viral
- Paid
INNOVATION
In order to improve innovation,
The team must be the first customer of the product.