By Jeff Sutherland & JJ Sutherland.
This post summarize the book SCRUM: The Art of Doing Twice the Work in Half the Time by Jeff Sutherland & JJ Sutherland. Is it really possible?
You can find the
SCRUM values : Courage, Focus, Commitment, Respect, Openness
Chapter 1: The Way the World Works is Broken
- Planning is Useful. Blindly following plans is stupid.
- Inspect and Adapt.
- Bring Teams together with the same Goal.
- Change or Die.
- Fail Fast so you Can Fix Early.
- Identify and correct what slow the team.
- Working product in short cycles allows early user feedback and eliminate what is obviously wasteful effort.
- The 80/20 rule.
Chapter 2: The Origins of Scrum
- OODA: Observe, Orient, Decide, Act.
- Waterfall and methodologies supported by lots of Gantt Chart are useless.
- Measure what exactly is being done, and how well, and to strive for ‘continuous improvement.
- Management should not dictate but FACILITATE.
- SHU-HA-RI – First, learn the rules and the forms, and once you’ve mastered them, make innovations. Finally, in a heightened state of mastery, discard the forms.
- Prioritize Quality.
- Hesitation is Death.
Chapter 3: Teams
- Scrum is based on teams.
- Transcendent (purpose), autonomous and cross-functionnal.
Questions to ask :
- 1. What did you since the last time we talked?
- 2. What are you going to do before we talk again?
- 3. And what is getting in your way?
- Team size: 7 persons ideal, 3 persons minimum. Anything greater than 9 will slow down the team’s velocity. Everyone in the team should know what everybody is doing.
- Instead of looking for blame, rewards positive behaviour and working together.
- Don’t look for bad people, look for bad systems.
Chapter 4: Time
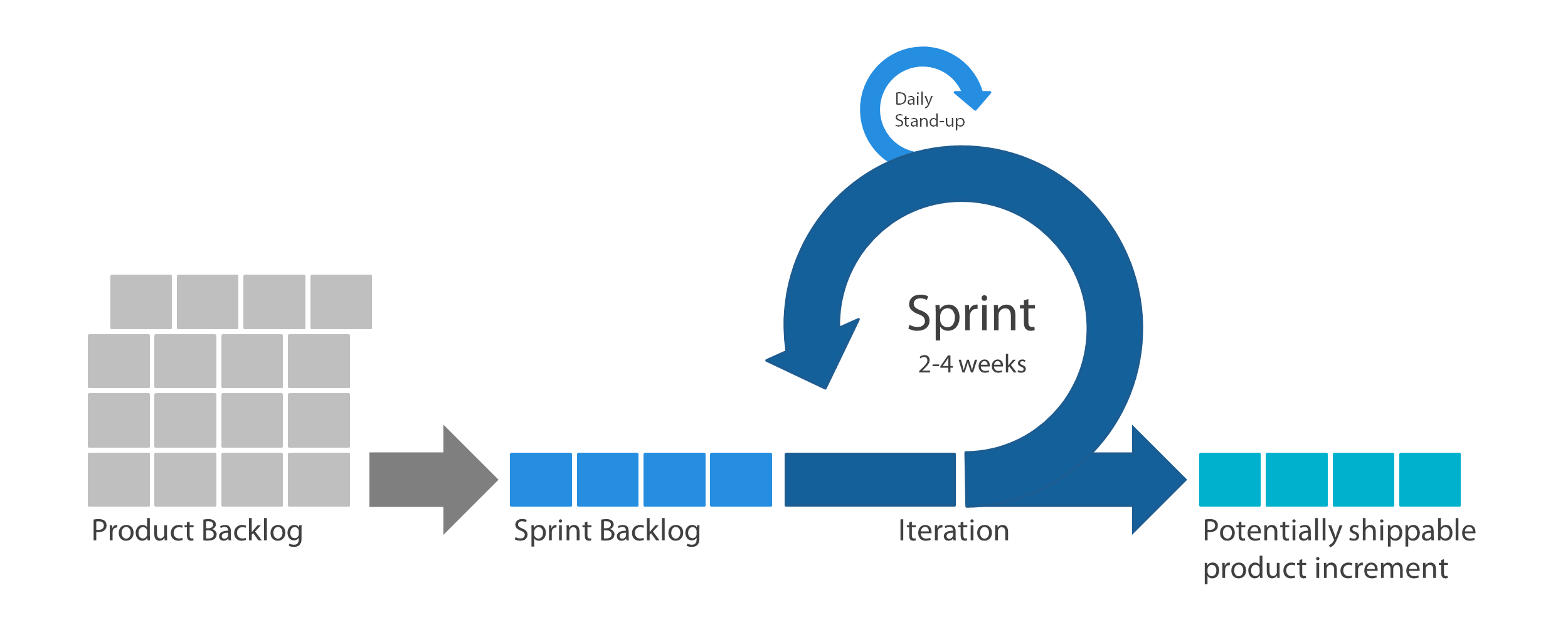
- Backlog –> To Do –> Doing –> DONE
Daily Stand-Up:
- What did you do yesterday to help the team finish the sprint?
- 2. What will you do today to help the team finish the sprint?
- 3. What obstacles are getting in the team’s way?
- Eliminate passivity.
- The greater the communication situation, the more everyone knows everything–the faster the team.
- People shouldn’t have a special TITLE.
- Meet every single day & get everyone together in a ROOM.
- People should discuss who does what and choose the tasks he wants to do.
- Each SPRINT is the opportunity to do something totally NEW.
Chapter 5: Waste is a Crime
- Muri – waste through unreasonableness – avoided by PLAN.
- Mura – waste through inconsistency – avoided by DO.
- Muda – waste through outcomes – avoided by CHECK.
- ACT – motivation to do all that.
- Do one thing at a time.
- Ban stupid policies.
- Do not give ABSURD goals. Work = Discipline + Flow.
- Problem: STOP everything and meet all the team to solve it. Solve immediately.
- MULTITASKING wastes your time & make you stupid.
- Jobs that aren’t done & Products that aren’t used is just WASTE.
- Working LATE is not a sign of commitment it is a sign of FAILURE – no energy and heroic efforts are
failure . - Don’t Be Unreasonable. Goals that are challenging are motivators; goals that are impossible are just depressing.
- No assholes. Don’t be one, and don’t allow the behaviour.
Chapter 6: Plan Reality, Not Fantasy
- How do you eat an elephant? One bite at a time!
- Decompose in little tasks.
- People must know that the features they work on will be USEFULL.
- You can’t plan everything ahead of time.
- The Map is Not the Terrain. Don’t fall in love with your plan. It’s almost certainly wrong.
- Only Plan What You Need To. Don’t try to project everything out years in advance. Just plan enough to keep your team busy.
- PRIORITIZE tasks – Define character, user and customer.
- ESTIMATE with Fibonacci. Poker sizing.
- Have your own judgement.
- If too much differences people talk.
- People doing the WORK know the time needed.
- Know Your Velocity. Every team should know exactly how much work they can get done in each Sprint.
- Set Audacious Goals.
Chapter 7: Happiness
- During Sprint Retrospective: look for what went right, what could have been done better, what can be made better next sprint.
- Implement improvements right away.
- Team happiness: Autonomy, Mastery, & Purpose.
- Scrum Master – keep the team from pride and complacency.
- It’s the Journey, Not the Destination. True happiness is found in the process, not the result.
- Quantify Happiness.
- At the end of each Sprint, the team should pick one small improvement – or kaizen.
- Nothing should be secret.
- Don’t forget performance.
Chapter 8: Priorities
- The Backlog should have everything that could possibly be included in the product.
- List everything.
- Product Vision is the intersection of “What you can implement”, “what you can be passionate about” and “What you can sell”.
- Aim for REVENUE first. 80/20 rule.
- “Will we make money doing this?”
- Build
MVP . - Figure out where the most value can be delivered for the least effort, and do that one right away. Then identify the next increment after that, and the next.
- 3 SCRUM roles: Product Owner, Scrum Master & Team members.
- Product Owner: Insert VISION in the backlog.
- Principles of MVP, Lean startup: TEST: put it to end-users as quickly as possible, get feedback, then iterate.
- Observe, Orient, Decide, Act (OODA).
- Create new things ONLY if they deliver value.
- What you thought
in the beginning is needed never end up to be actually needed.
Chapter 9: Change the World
- SCRUM can be used in everything to improve performance & results.
- SCRUM can be used in school (ex: Netherlands).
- Get rid of all titles, managers, structures, process.
- Give people the freedom to do what they think best and the responsibility to be accountable for it.